IRF9540NSTRLPBF new and original Integrated circuits Electronic components
Product Attributes
| TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
| Category | Discrete Semiconductor Products |
| Mfr | Infineon Technologies |
| Series | HEXFET® |
| Package | Tape & Reel (TR)
Cut Tape (CT) Digi-Reel® |
| Product Status | Active |
| FET Type | P-Channel |
| Technology | MOSFET (Metal Oxide) |
| Drain to Source Voltage (Vdss) | 100 V |
| Current – Continuous Drain (Id) @ 25°C | 23A (Tc) |
| Drive Voltage (Max Rds On, Min Rds On) | 10V |
| Rds On (Max) @ Id, Vgs | 117mOhm @ 14A, 10V |
| Vgs(th) (Max) @ Id | 4V @ 250µA |
| Gate Charge (Qg) (Max) @ Vgs | 110 nC @ 10 V |
| Vgs (Max) | ±20V |
| Input Capacitance (Ciss) (Max) @ Vds | 1450 pF @ 25 V |
| FET Feature | - |
| Power Dissipation (Max) | 3.1W (Ta), 110W (Tc) |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 150°C (TJ) |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount |
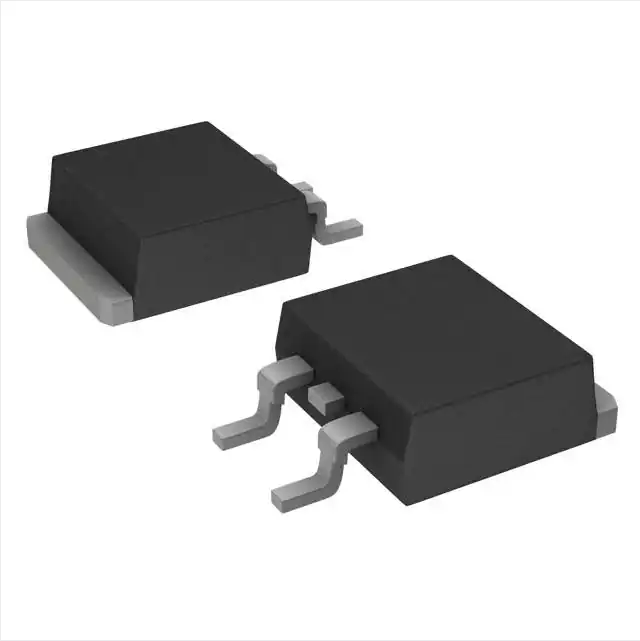
| Supplier Device Package | D2PAK |
| Package / Case | TO-263-3, D²Pak (2 Leads + Tab), TO-263AB |
| Base Product Number | IRF9540 |
Documents & Media
| RESOURCE TYPE | LINK |
| Datasheets | IRF9540NS/L |
| Other Related Documents | IR Part Numbering System |
| Product Training Modules | High Voltage Integrated Circuits (HVIC Gate Drivers) |
| Featured Product | Data Processing Systems |
| HTML Datasheet | IRF9540NS/L |
| EDA Models | IRF9540NSTRLPBF by Ultra Librarian |
| Simulation Models | IRF9540NL Saber Model |
Environmental & Export Classifications
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
| RoHS Status | ROHS3 Compliant |
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 1 (Unlimited) |
| REACH Status | REACH Unaffected |
| ECCN | EAR99 |
| HTSUS | 8541.29.0095 |
IRF9540NS
-100V Single P-Channel IR MOSFET in a D2-Pak package
Benefits
- Planar cell structure for wide SOA
- Optimized for broadest availability from distribution partners
- Product qualification according to JEDEC standard
- Silicon optimized for applications switching below <100kHz
- Industry standard surface-mount power package
- High-current carrying capability package (up to 195 A, die-size dependent)
- Capable of being wave-soldered
Discrete Semiconductor Device
Different semiconductors are sold out as part of essential circuits, frequently on an IC. These circuits can generally carry about continuous functions and features in a device, substantially differentiating them from significant discrete semiconductors.
Most semiconductors are bought as an essential part of circuits in today’s world. However, for some applications, a discrete semiconductor offers the best solutions for the need of engineering. Therefore, they also play a vital role in electronic components in the marketplace. Yes, you heard that right!
The primary examples are thyristors, transistors, rectifiers, diodes, and many versions of these efficient devices. Other structures of semiconductors with the integrated circuits’ physical complexity but performing electronic functions like Darlington transistors are typically considered discrete semiconductor machines.
Discrete Semiconductor Device | High-end Benefits
There are a lot of top-notch benefits of super cool discrete semiconductor devices. Some of them are listed below:
- All the discrete semiconductor devices are highly compact and lightweight.
- They are highly reliable because of their low power consumption and appropriate size.
- They can be conveniently replaced. However, their replacement is a bit tough due to the absence of capacitance and parasitic effect.
- There are minor temperature differences between its circuit components.
- It is best suitable for a lot of small-signal operations.
- These devices reduce power consumption because of their highly compact and suitable size.
A discrete semiconductor performs incredibly functions that can’t be divided into other parts. For instance, an IC may have a diode, a transistor, and other essential components that can easily do various tasks independently. They can also work in conjunction with the outstanding circuit and perform many functions.
Conversely, the discrete semiconductor can perform a single function. For example, a transistor is always an exemplary transistor & can perform its function associated with only the transistor.
This article contains all the essential information, including its benefits, drawbacks, and top-notch examples – so that you can get utterly familiar with discrete semiconductor devices.